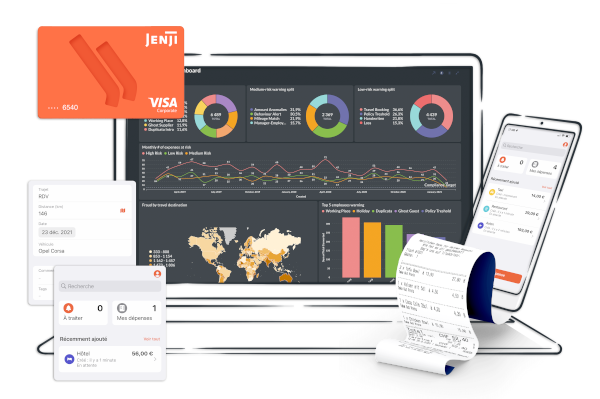
Jenji, votre logiciel de notes de frais
Plus de 40 000 organisations font confiance à Jenji

































Automatisation
Tous vos reçus et factures sont traités automatiquement, sans erreurs, ce qui assure la qualité de vos données et optimise également vos workflow validation.
En savoir plus
Zéro Papier
Celle-ci permet à votre entreprise d'adopter une démarche écologique, productive et économique en passant au zéro papier.
En savoir plus
Intelligence Artificielle
L'Intelligence Artificielle permet de les analyser pour avoir une optimisation précise de vos processus et une vue globale sur vos dépenses.
En savoir plus.png?width=340&name=Integrations%20(1).png)
Intégration
Notre suite de solution Jenji Advisor intègre toutes vos sources de données internes et externes en un seul et même point. Vous avez alors les clés pour travailler sur l'analyse et corriger ce qui est nécessaire.
En savoir plus
Satisfaction
Nos équipes sont mobilisées autour des besoins et vous aident à avoir une vision 360° de votre projet de transformation.
En savoir plusGérer vos notes de frais en temps réel
Qui utilise notre logiciel de note de frais ?
Collaborateur
Vous êtes fatigué de collecter tous vos tickets et d'attendre d'être remboursé ?
Pour plus de facilité et de rapidité, nous mettons à votre disposition une application mobile ainsi qu'une Web App. Vos notes de frais sont soumises, validées et remboursées automatiquement. Un seul mot d'ordre : l'efficacité.
Responsable financier
Vous êtes-vous déjà demandé comment optimiser votre politique de dépenses ?
Avec l'aide de puissants outils d'analyse financière qui intègrent toutes vos données en un seul endroit, vous pouvez améliorer vos prévisions et rapports financiers.
Cette simplification apporte transparence pour transformer vos dépenses en une source de profit.
Responsable comptabilité
Vous souhaitez arrêter de passer des heures à calculer quelles taxes peuvent être récupérées ?
Jenji calcule ce montant automatiquement en fonction des règles de comptabilité analytique de votre organisation mais aussi celles du pays en vigueur, afin que vous puissiez être sûr que tout est en ordre.
quatre étapes
Comment gérer avec succès ses notes de frais ?
Rédiger une politique de dépenses claire
Il est essentiel d'avoir une politique de dépenses formelle pour votre entreprise. Elle aide avant tout l'équipe dirigeante à déterminer comment les collaborateurs peuvent utiliser l'argent de l'entreprise.
Proposer des modes de paiement adaptés
Être vraiment efficace dans le contrôle des dépenses des collaborateurs n'est pas simple. La meilleure solution est de leur proposer un mode de paiement sur mesure qui allie flexibilité et sécurité.
Numériser et automatiser les processus
Pour accélérer ses processus et éviter de perdre du temps à collecter les factures, il est intéressant de numériser la collecte des reçus. Les reçus électroniques sont acceptés légalement dans le monde entier.
COMMENT PROFITER DE JENJI
Plus qu'une simple application pour les notes de frais
Jenji Studio
Analyse des dépenses
Comment obtenir une vision globale de vos dépenses ?
En savoir plusJenji Advisor Suite
Profondeur d'analyse
Analyser et optimiser votre processus budgétaire
En savoir plusJenji Vault
Stockage des données
La dématérialisation permet de gagner du temps et de l'espace, mais aussi de réduire ses impressions et émissions carbone. Quels sont les avantages de l'archivage numérique ?
Avantages de l'archivage numériqueJenji Pay
Paiement simplifié
Comment éviter les retards de soumission et avoir le contrôle sur vos transactions ?
Sécurisez vos paiements
Jenji Connect
Portail personnalisé
Un nouveau collaborateur rejoint votre entreprise ? Jenji Connect vous permet d'ajouter facilement un nouvel utilisateur à votre compte Jenji en quelques clics.
![]()
Voir comment cela fonctionne

EXPENSE MANAGEMENT INDEX #3
De la gestion des dépenses à la mobilité durable
Jenji lance son troisième Expense Management Index et met à l'honneur la question des déplacements verts et son évolution.
Obtenez de nouvelles analyses clés du secteur de la gestion des frais grâce au dernier indice Jenji !

Pourquoi choisir le logiciel de note de frais Jenji ?
Solution de paiement
Le paiement virtuel a augmenté de 40 % en seulement deux ans.
Dématérialisation
On estime qu'il faut 24 arbres pour fabriquer une tonne de papier de bureau standard
Un outil tout en un
Les grandes entreprises utilisent aujourd'hui en moyenne 37 outils ou plateformes logicielles différents pour mener à bien leurs opérations quotidiennes.

DÉCOUVREZ notre guide
Guide de la note de frais
Si vous êtes chargés de mettre en place une stratégie de gestion de note de frais pour le compte de votre entreprise, si vous êtes à la recherche d’un outil de gestion de note de frais qui vous facilite la vie, ce guide est pour vous.
Pour tout savoir sur la note de frais





